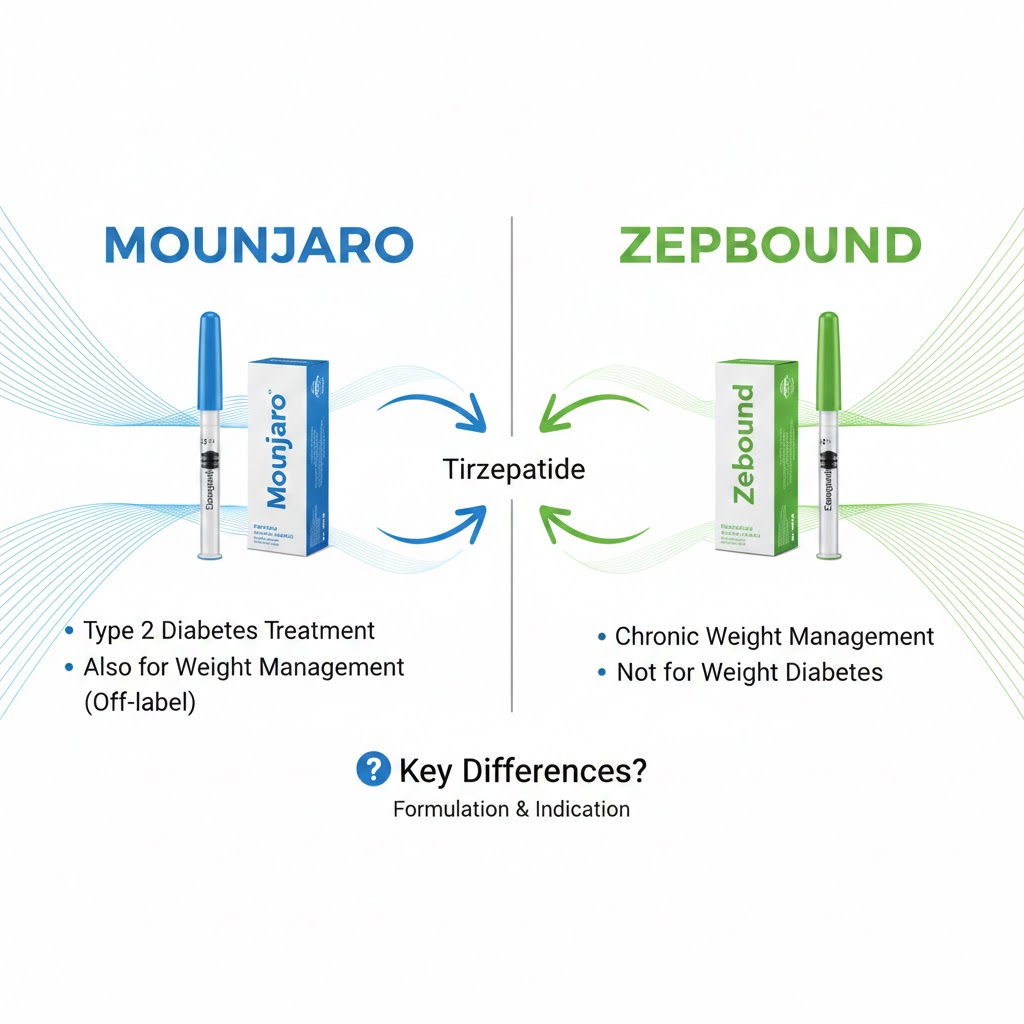
Mounjaro vs Zepbound are injectable prescription medications that contain the same active ingredient, tirzepatide, but they are approved for different medical purposes. Both drugs belong to a newer class of treatments that target metabolic health by improving blood sugar control and promoting significant weight loss. Despite their similarities, the difference between Mounjaro and Zepbound lies in their approved use, prescribing guidelines, and insurance coverage.
Understanding these differences is important for patients deciding which treatment is appropriate for diabetes management or weight loss.
How Tirzepatide Works
Tirzepatide is a dual GLP-1 and GIP receptor agonist, meaning it activates two key hormone pathways involved in glucose regulation and appetite control.
Mechanism of action
- Enhances insulin secretion in response to meals
- Reduces glucagon release, lowering blood sugar levels
- Slows gastric emptying, leading to prolonged fullness
- Suppresses appetite and reduces calorie intake
By targeting both GLP-1 and GIP receptors, tirzepatide produces stronger metabolic effects than older GLP-1–only medications.
What Is Mounjaro?
Mounjaro is FDA-approved for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Its primary goal is to improve blood sugar control, with weight loss considered a secondary benefit.
Approved use
- Type 2 diabetes in adults
Key benefits
- Significant reduction in HbA1c levels
- Improved insulin sensitivity
- Consistent and meaningful weight loss
Although weight loss is common with Mounjaro, it is prescribed specifically for diabetes management. Any use for weight loss alone is considered off-label in many regions.
What Is Zepbound?
Zepbound is FDA-approved specifically for chronic weight management in adults who are obese or overweight with at least one weight-related medical condition.
Approved use
- Chronic weight management
Eligibility criteria
- Body mass index (BMI) ≥30 (obesity), or
- BMI ≥27 with conditions such as hypertension, dyslipidemia, or type 2 diabetes
Zepbound focuses on long-term weight reduction and maintenance rather than blood sugar control, although it also improves metabolic markers.
Key Differences Between Mounjaro and Zepbound
Mounjaro vs Zepbound Although both medications contain tirzepatide, they differ in clinical positioning.
Primary indication
- Mounjaro: Type 2 diabetes
- Zepbound: Weight loss
Prescribing intent
- Mounjaro prioritizes glycemic control
- Zepbound prioritizes sustained weight reduction
Insurance coverage
- Mounjaro is often covered under diabetes treatment plans
- Zepbound coverage depends on obesity or weight-management benefits
Patient population
- Mounjaro is intended for diabetic patients
- Zepbound targets non-diabetic and diabetic patients seeking weight loss
Weight Loss Effectiveness
Both drugs result in substantial weight loss due to their identical active ingredient.
Clinical observations
- Average weight loss can exceed 15–20% of body weight
- Appetite suppression increases with dose escalation
- Weight loss is typically gradual and sustained
In clinical trials, weight loss outcomes with Zepbound are emphasized, while Mounjaro trials focus primarily on glucose control, even though weight loss results are comparable.
Blood Sugar Control
Mounjaro is specifically optimized for glucose regulation.
Effects on diabetes
- Significant HbA1c reduction
- Improved fasting and post-meal glucose levels
- Reduced need for additional diabetes medications in some patients
Zepbound may also lower blood sugar, but it is not prescribed solely for diabetes treatment.
Side Effects of Mounjaro and Zepbound
Mounjaro vs Zepbound Because both medications contain tirzepatide, their side effect profiles are nearly identical.
Common Side Effects
Most side effects occur during dose escalation and often improve over time.
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Abdominal discomfort
- Decreased appetite
- Fatigue
Serious Side Effects and Warnings
Although less common, serious side effects can occur.
Gastrointestinal complications
- Severe or persistent vomiting
- Dehydration
Gallbladder issues
- Gallstones associated with rapid weight loss
Pancreatitis
- Severe abdominal pain radiating to the back
Thyroid tumor risk
- Contraindicated in patients with a personal or family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma or MEN2
Patients should be monitored closely, especially during dose increases.
Dosing and Administration
Both medications are administered as once-weekly subcutaneous injections.
Dosing structure
- Gradual dose escalation to improve tolerability
- Maintenance dose selected based on response and side effects
Injection sites include the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm.
Who Should Use Each Medication
Mounjaro may be preferred if
- The primary goal is diabetes control
- HbA1c reduction is the top priority
- Insurance coverage favors diabetes medications
Zepbound may be preferred if
- The primary goal is weight loss
- The patient does not have diabetes
- Long-term weight management is required
A healthcare provider determines suitability based on medical history and treatment goals.
Conclusion
Mounjaro and Zepbound are closely related medications that use the same active ingredient but serve different clinical purposes. Mounjaro is designed for managing type 2 diabetes, while Zepbound is approved specifically for chronic weight loss. Both offer powerful metabolic benefits, including significant weight reduction, but the choice between them depends on treatment goals, diagnosis, and insurance coverage.
When used appropriately under medical supervision, both medications represent a major advancement in the treatment of diabetes and obesity.
More Related Topics:
Eliquis Uses as a Blood Thinner: Benefits and Risks
Ozempic vs Wegovy: Which Semaglutide Is Better for Weight Loss?