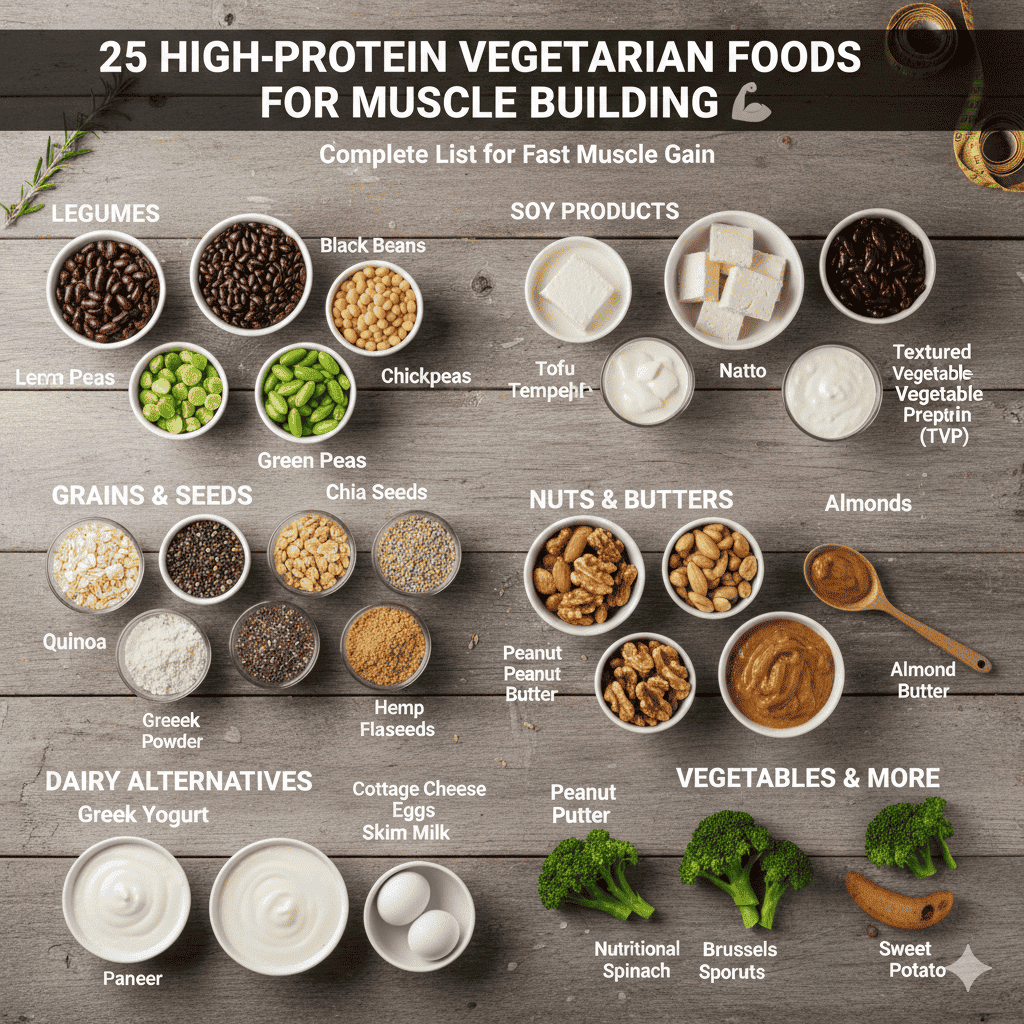
Building muscle on a vegetarian diet is not only possible but can be incredibly effective when you know which foods to include. Many people believe that animal products are essential for muscle growth, but the truth is that high-protein vegetarian foods can provide all the nutrients your muscles need to grow stronger and larger. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the best protein sources available to vegetarians, complete with nutritional information and practical tips for incorporating them into your daily routine.
Understanding Protein Requirements for Muscle Building
Before diving into specific high-protein vegetarian foods, it’s important to understand how much protein you actually need. For muscle building, research suggests that individuals should consume between 1.6 to 2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight daily. This means a 70-kilogram person would need approximately 112 to 154 grams of protein each day.
The key to successful muscle building on a vegetarian diet lies in consuming complete proteins or combining complementary proteins throughout the day. Complete proteins contain all nine essential amino acids that your body cannot produce on its own. While many animal products are complete proteins, several vegetarian sources also meet this criterion, and strategic combinations of incomplete proteins can provide the full amino acid profile your muscles require.
1. Greek Yogurt: The Protein Powerhouse
Greek yogurt stands out as one of the most versatile high-protein vegetarian foods available. A single cup of plain Greek yogurt can contain 15 to 20 grams of protein, making it an excellent choice for muscle building.
Benefits for muscle growth:
- Contains both whey and casein proteins for sustained amino acid release
- Rich in probiotics that support gut health and nutrient absorption
- High in calcium for bone strength during intense training
- Provides B vitamins essential for energy metabolism
How to incorporate it: Mix Greek yogurt with berries and nuts for a post-workout snack, use it as a base for protein smoothies, or substitute it for sour cream in savory dishes to boost protein content without adding extra calories.
2. Lentils: The Versatile Legume Champion
Lentils are among the most accessible and affordable high-protein vegetarian foods you can find. One cup of cooked lentils delivers approximately 18 grams of protein along with significant amounts of fiber and complex carbohydrates.
Nutritional advantages:
- Excellent source of iron for oxygen transport to muscles
- Contains folate and other B vitamins
- Provides slow-digesting carbohydrates for sustained energy
- Rich in polyphenols with anti-inflammatory properties
Preparation suggestions: Add lentils to soups and stews, create lentil-based burgers, prepare Indian dal dishes, or toss cooked lentils into salads for an instant protein boost.
3. Quinoa: The Complete Protein Grain
Quinoa deserves special recognition among high-protein vegetarian foods because it’s one of the few plant-based complete proteins. One cup of cooked quinoa provides about 8 grams of protein with all essential amino acids.
Why quinoa excels:
- Contains lysine, often lacking in plant proteins
- Gluten-free option for those with sensitivities
- High in magnesium for muscle function and recovery
- Provides manganese and phosphorus for bone health
Culinary applications: Use quinoa as a rice substitute, create quinoa breakfast porridge, add it to veggie burgers, or prepare quinoa salad bowls with vegetables and tahini dressing.
4. Cottage Cheese: The Slow-Release Protein Source
Cottage cheese is an underrated champion among high-protein vegetarian foods, offering 14 grams of protein per half-cup serving. Its high casein content makes it particularly valuable for muscle building.
Muscle-building benefits:
- Casein provides slow amino acid release for overnight muscle repair
- Low in calories relative to protein content
- Contains leucine, the key amino acid for muscle protein synthesis
- Rich in calcium and phosphorus
Serving ideas: Eat cottage cheese before bed for overnight muscle recovery, blend it into smoothies for creaminess and protein, mix with fruit for a quick snack, or use it in savory dishes as a ricotta substitute.
5. Chickpeas: The Mediterranean Muscle Builder
Chickpeas, also known as garbanzo beans, are fantastic high-protein vegetarian foods that provide 15 grams of protein per cooked cup. They’re incredibly versatile and form the base of many traditional dishes.
Nutritional profile:
- High in complex carbohydrates for workout fuel
- Contains significant amounts of folate and iron
- Provides fiber for digestive health and satiety
- Rich in manganese and copper
Recipe ideas: Make traditional hummus, roast chickpeas for crunchy snacks, add them to curries and stews, prepare chickpea flour pancakes, or create falafel for protein-rich meals.
6. Tofu: The Adaptable Protein Block
Tofu is perhaps the most famous among high-protein vegetarian foods, and for good reason. A 100-gram serving of firm tofu contains approximately 10 grams of protein, and it absorbs flavors beautifully.
Health advantages:
- Complete protein with all essential amino acids
- Contains isoflavones that may support bone health
- Low in saturated fat compared to many protein sources
- Provides iron and calcium when prepared with calcium sulfate
Cooking methods: Press and marinate tofu before grilling or baking, scramble it as an egg alternative, add cubed tofu to stir-fries, blend silken tofu into smoothies, or create tofu-based desserts.
7. Black Beans: The Fiber-Protein Combination
Black beans are outstanding high-protein vegetarian foods that deliver 15 grams of protein per cooked cup alongside impressive fiber content. They’re particularly popular in Latin American cuisine.
Nutritional highlights:
- Excellent source of molybdenum for amino acid metabolism
- High in antioxidants, particularly anthocyanins
- Provides thiamin for energy production
- Contains resistant starch that supports gut health
Meal suggestions: Prepare black bean tacos or burritos, make black bean soup, create veggie burgers with black beans as the base, add them to rice bowls, or prepare Brazilian feijoada.
8. Edamame: The Young Soybean Sensation
Edamame represents one of the most enjoyable high-protein vegetarian foods to eat. One cup of shelled edamame provides 17 grams of complete protein, making it exceptional for muscle building.
Performance benefits:
- Contains all nine essential amino acids
- Rich in folate for cell growth and repair
- Provides vitamin K for bone health
- High in fiber and healthy fats
Serving suggestions: Steam edamame pods and sprinkle with sea salt for snacking, add shelled edamame to salads and grain bowls, blend into hummus alternatives, or stir-fry with vegetables.
9. Tempeh: The Fermented Protein Powerhouse
Tempeh is a fermented soy product that ranks among the most nutrient-dense high-protein vegetarian foods available. A 100-gram serving contains about 19 grams of protein with superior digestibility due to fermentation.
Unique advantages:
- Fermentation increases nutrient bioavailability
- Contains probiotics for gut health
- Provides vitamin B12, rare in plant foods
- Higher in protein than tofu
Preparation methods: Marinate and grill tempeh slices, crumble it into pasta sauces like ground meat, cube and add to stir-fries, make tempeh bacon, or create tempeh-based sandwich fillings.
10. Hemp Seeds: The Tiny Protein Giants
Hemp seeds are remarkable high-protein vegetarian foods that provide 10 grams of protein per three tablespoons. They’re also one of few plant sources containing complete protein.
Nutritional excellence:
- Perfect omega-3 to omega-6 fatty acid ratio
- Easily digestible protein
- Rich in gamma-linolenic acid for inflammation reduction
- Contains vitamin E and minerals like phosphorus and potassium
Usage tips: Sprinkle hemp seeds on yogurt or oatmeal, blend into smoothies, add to salad dressings, incorporate into energy balls, or use hemp protein powder in shakes.
11. Chia Seeds: The Ancient Superfood
Chia seeds are incredible high-protein vegetarian foods that pack 5 grams of protein per two tablespoons along with exceptional omega-3 fatty acid content. They also create a gel-like consistency when mixed with liquid.
Health properties:
- High in alpha-linolenic acid for heart health
- Provides sustained energy release
- Rich in antioxidants and minerals
- Excellent source of soluble fiber
Creative uses: Make chia pudding for breakfast or dessert, add to smoothies for thickness and nutrition, create chia jam without added sugar, sprinkle on cereal or yogurt, or use as an egg substitute in baking.
12. Pumpkin Seeds: The Mineral-Rich Snack
Pumpkin seeds, or pepitas, are outstanding high-protein vegetarian foods containing 7 grams of protein per ounce. They’re particularly rich in minerals crucial for muscle function.
Mineral content:
- Exceptional source of magnesium for muscle relaxation and energy
- High in zinc for testosterone production and immune function
- Contains iron and manganese
- Provides tryptophan for better sleep and recovery
Snacking ideas: Roast pumpkin seeds with spices, add to trail mix, sprinkle on salads and soups, blend into pesto, or incorporate into homemade protein bars.
13. Peanut Butter: The Classic Protein Spread
Natural peanut butter remains one of the most popular high-protein vegetarian foods, providing 8 grams of protein per two-tablespoon serving. It’s affordable, accessible, and incredibly versatile.
Nutritional benefits:
- Contains healthy monounsaturated fats
- Rich in resveratrol, an antioxidant
- Provides niacin for energy metabolism
- High in vitamin E for cell protection
Application methods: Spread on whole grain toast or rice cakes, blend into protein shakes, use as a dip for apple slices or celery, add to oatmeal, or incorporate into Asian-inspired sauces.
14. Almonds: The Heart-Healthy Protein Source
Almonds are nutrient-dense high-protein vegetarian foods that provide 6 grams of protein per ounce along with exceptional vitamin E content. They make an excellent portable snack for active individuals.
Nutritional profile:
- High in vitamin E for oxidative stress reduction
- Contains magnesium for muscle and nerve function
- Provides healthy fats for hormone production
- Rich in biotin for energy metabolism
Consumption methods: Eat raw almonds as snacks, make homemade almond butter, use almond flour in baking, drink almond milk, or add sliced almonds to salads and stir-fries.
15. Spirulina: The Algae Protein Supplement
Spirulina is an extraordinary addition to high-protein vegetarian foods, containing about 8 grams of protein per two tablespoons. This blue-green algae is one of the most nutrient-dense foods on Earth.
Unique composition:
- Contains all essential amino acids
- Extremely high in B vitamins, particularly B12
- Rich in iron and copper
- Provides powerful antioxidants like phycocyanin
Integration strategies: Add spirulina powder to smoothies, mix into energy balls, incorporate into salad dressings, blend with guacamole, or take spirulina tablets as supplements.
16. Nutritional Yeast: The Cheesy Protein Booster
Nutritional yeast is a deactivated yeast that’s become one of the favorite high-protein vegetarian foods among plant-based athletes. Two tablespoons provide 8 grams of complete protein.
Functional benefits:
- Fortified with vitamin B12 in most brands
- Contains glutathione for antioxidant protection
- Provides trace minerals including zinc and selenium
- Adds savory, cheese-like flavor to dishes
Culinary applications: Sprinkle on popcorn for a cheesy flavor, add to pasta dishes, blend into cashew cheese sauces, mix into mashed potatoes, or use as a parmesan substitute.
17. Seitan: The Wheat Meat Alternative
Seitan, made from wheat gluten, is one of the highest-protein high-protein vegetarian foods available, containing 25 grams of protein per 100 grams. It has a meat-like texture that many people appreciate.
Protein characteristics:
- Extremely high protein density
- Low in fat and carbohydrates
- Versatile texture that mimics meat
- Absorbs marinades and seasonings well
Cooking approaches: Make homemade seitan for cost savings, grill or pan-fry for sandwiches, use in stir-fries, create seitan-based stews, or prepare as mock duck or chicken alternatives.
18. Green Peas: The Humble Protein Vegetable
Green peas often surprise people when listed among high-protein vegetarian foods, but one cup of cooked peas provides 8 grams of protein along with vitamins and minerals.
Nutritional advantages:
- High in vitamin K for bone health
- Contains vitamin C for collagen synthesis
- Provides folate and other B vitamins
- Rich in lutein for eye health
Serving methods: Add to pasta dishes and risottos, blend into soups, include in fried rice, make pea protein smoothies, or prepare mushy peas as a traditional side dish.
19. Oats: The Muscle-Building Breakfast Staple
Oats are exceptional high-protein vegetarian foods that provide sustained energy along with 6 grams of protein per cup when cooked. They’re perfect for pre-workout meals.
Performance benefits:
- Contains beta-glucan for heart health and immune function
- Provides slow-release carbohydrates for sustained energy
- Rich in iron, magnesium, and zinc
- High in soluble fiber for digestive health
Preparation ideas: Make overnight oats with protein powder, prepare savory oatmeal with vegetables and nutritional yeast, create protein-rich granola, bake oatmeal breakfast bars, or blend oats into smoothies.
20. Buckwheat: The Gluten-Free Protein Grain
Despite its name, buckwheat isn’t related to wheat and is actually a complete protein. This makes it one of the valuable high-protein vegetarian foods for those avoiding gluten, with 6 grams of protein per cooked cup.
Health properties:
- Contains all essential amino acids
- Rich in rutin for blood vessel strength
- Provides resistant starch for gut health
- High in manganese and magnesium
Usage suggestions: Make buckwheat pancakes or crepes, prepare soba noodles, cook buckwheat porridge, use in grain bowls, or incorporate into baked goods.
21. Amaranth: The Ancient Grain Protein
Amaranth is an ancient pseudocereal that qualifies as one of the complete high-protein vegetarian foods, providing 9 grams of protein per cooked cup. It was a staple food of the Aztecs.
Nutritional composition:
- Contains lysine, often limiting in grains
- High in calcium compared to other grains
- Rich in squalene, a beneficial compound
- Provides significant amounts of iron and magnesium
Cooking methods: Pop amaranth like popcorn for a crunchy topping, cook as a breakfast porridge, add to soups for thickness, mix with other grains, or use amaranth flour in gluten-free baking.
22. Ezekiel Bread: The Sprouted Grain Protein
Ezekiel bread and similar sprouted grain breads are unique among high-protein vegetarian foods because sprouting increases protein availability. Two slices provide about 8 grams of protein.
Sprouting benefits:
- Increased nutrient bioavailability
- Easier to digest than regular bread
- Contains complete protein from grain and legume combination
- Lower glycemic index than conventional bread
Meal integration: Use for protein-rich toast with nut butter, make sandwiches with hummus and vegetables, prepare French toast with added eggs, use as a base for avocado toast, or cube and make sprouted grain croutons.
23. Pea Protein Powder: The Hypoallergenic Option
Pea protein powder has emerged as one of the most popular high-protein vegetarian foods for athletes, providing 20 to 25 grams of protein per scoop. It’s particularly valuable for those with dairy or soy allergies.
Advantages for athletes:
- Highly digestible and hypoallergenic
- Rich in branched-chain amino acids
- Supports muscle growth comparable to whey protein
- Environmentally sustainable protein source
Application methods: Blend into post-workout smoothies, mix into oatmeal or yogurt, add to baked goods for extra protein, create protein pancakes, or make protein energy balls.
24. Mung Beans: The Asian Protein Staple
Mung beans are versatile high-protein vegetarian foods commonly used in Asian cuisine, providing 14 grams of protein per cooked cup. They’re easier to digest than many other legumes.
Digestive benefits:
- Lower in oligosaccharides that cause gas
- Rich in folate for cell division and growth
- Contains antioxidant vitexin
- Provides significant amounts of manganese and magnesium
Preparation options: Sprout mung beans for salads, cook into dal or curry, make mung bean pancakes, prepare traditional Asian desserts, or add to soups and stews.
25. Fava Beans: The Mediterranean Protein Choice
Fava beans, also known as broad beans, round out our list of high-protein vegetarian foods with 13 grams of protein per cooked cup. They’re particularly popular in Middle Eastern and Mediterranean cuisines.
Nutritional highlights:
- Excellent source of l-dopa, a dopamine precursor
- High in folate and manganese
- Contains copper for energy production
- Rich in dietary fiber
Recipe suggestions: Prepare traditional falafel, make Egyptian ful medames, roast fava beans for snacking, add to salads and grain bowls, or create fava bean hummus.
Maximizing Muscle Growth with High-Protein Vegetarian Foods
Successfully building muscle on a vegetarian diet requires more than just eating high-protein vegetarian foods. You need to consider timing, combination, and overall dietary strategy to optimize muscle protein synthesis and recovery.
Protein timing strategies: Distribute protein intake evenly across meals rather than loading it all into dinner. Aim for 20 to 30 grams of protein per meal, which appears to maximize muscle protein synthesis. Consuming protein within two hours after resistance training can enhance recovery, though the overall daily intake matters more than precise timing.
Combining complementary proteins: While it’s no longer believed necessary to combine complementary proteins in the same meal, eating a variety of high-protein vegetarian foods throughout the day ensures you get all essential amino acids. Classic combinations include rice and beans, hummus and whole grain pita, or peanut butter on whole wheat bread.
Supporting nutrient considerations: Focus on getting adequate calories to support muscle growth, as building muscle requires energy surplus. Ensure sufficient intake of vitamin B12 through fortified foods or supplements, get enough iron from legumes and dark leafy greens paired with vitamin C, and maintain adequate zinc intake from seeds, nuts, and whole grains.
Creating Your High-Protein Vegetarian Meal Plan
Building muscle requires consistency and planning. Design your meal plan around high-protein vegetarian foods while ensuring variety to prevent nutritional deficiencies and taste fatigue.
Sample daily structure: Start your day with Greek yogurt topped with hemp seeds, chia seeds, and berries alongside whole grain toast with almond butter. For lunch, prepare a quinoa bowl with black beans, roasted vegetables, and tahini dressing. Afternoon snacks might include hummus with vegetables and roasted chickpeas. Dinner could feature tempeh stir-fry with edamame, served over brown rice, followed by a pre-bed cottage cheese bowl with pumpkin seeds.
Meal preparation strategies: Batch cook legumes and grains on weekends to streamline daily meal preparation. Keep protein-rich snacks readily available, such as roasted nuts, protein bars made with seeds and dates, or pre-portioned Greek yogurt. Prepare versatile protein bases like seasoned tofu, marinated tempeh, or cooked lentils that can be added to various meals throughout the week.
Supplementation considerations: While whole food high-protein vegetarian foods should form the foundation of your diet, protein powder can be convenient for meeting higher protein needs. Consider pea protein, brown rice protein, or hemp protein powders. Additionally, ensure adequate vitamin B12, vitamin D, and omega-3 fatty acids through fortified foods or supplements.
Tracking Progress and Adjusting Your Approach
Monitor your muscle-building progress to determine if your intake of high-protein vegetarian foods is adequate for your goals. Keep track of strength gains in the gym, take regular body measurements, and assess energy levels during workouts.
Signs you’re on track: Progressive strength increases, improved muscle definition, adequate energy for training sessions, good recovery between workouts, and stable or increasing body weight if that’s your goal all indicate your protein intake and overall nutrition are supporting muscle growth.
When to adjust: If you’re not seeing progress after several weeks, consider increasing your protein intake by 10 to 20 grams daily, ensuring you’re eating enough total calories, varying your high-protein vegetarian foods for complete amino acid coverage, and optimizing your training program alongside nutrition.
Conclusion
Building impressive muscle on a vegetarian diet is entirely achievable when you strategically incorporate these 25 high-protein vegetarian foods into your daily nutrition plan. From Greek yogurt and lentils to spirulina and fava beans, the plant-based world offers abundant protein sources that can rival or exceed the muscle-building potential of animal products.
The key to success lies in variety, consistency, and adequate total protein intake distributed throughout the day. By combining different high-protein vegetarian foods, you’ll ensure complete amino acid profiles while enjoying diverse flavors and textures that keep meals interesting and sustainable long-term.
Remember that muscle building requires patience, progressive resistance training, adequate rest, and proper nutrition working in harmony. These protein-rich vegetarian foods provide the building blocks your muscles need, but they must be paired with consistent training and recovery practices. Start incorporating more of these foods into your diet today, experiment with new recipes and combinations, and watch your strength and muscle mass grow on a completely vegetarian nutrition plan.
Also read this:
10 Daily Exercises to Reduce Belly Fat Naturally — Fast Results Without Dieting
7-Day Home Workout Plan for Beginners (No Equipment Needed) to Burn Fat & Build Strength Fast
7 AI Graphic Design Tools That Create Logos, Posters, and Brand Kits in Minutes