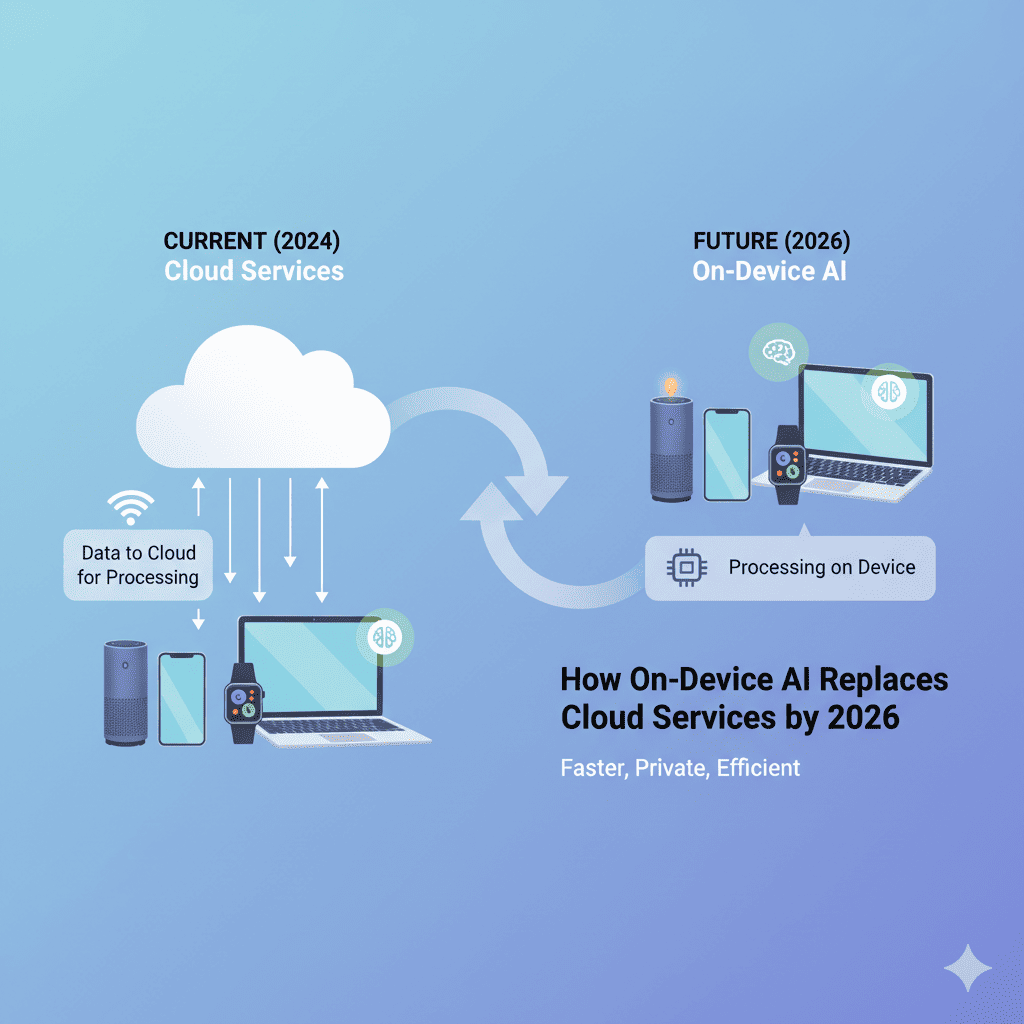
A quiet revolution is unfolding in your pocket, on your laptop, and across every connected device you own. On-Device AI Will Replace Cloud Services in ways that will fundamentally transform how we interact with technology, protect our privacy, and experience computing power. This isn’t a distant possibility—it’s happening right now, and by 2026, the landscape of artificial intelligence will look dramatically different from today.
For years, we’ve accepted a simple trade-off: send our data to the cloud, wait for powerful servers to process it, and receive results back. This model has powered everything from voice assistants to photo editing, language translation to recommendation engines. But On-Device AI Will Replace Cloud Services because the technology has reached an inflection point where local processing matches or exceeds cloud capabilities for many tasks—all while keeping your data private, working offline, and responding instantly.
The implications are staggering. Imagine AI that works on airplanes, in remote locations, and during internet outages. Picture powerful language models, image generators, and productivity tools that never send your data beyond your device. Consider the cost savings, security improvements, and performance gains when AI computation happens locally rather than in distant data centers.
The Technology Making On-Device AI Possible
The reason On-Device AI Will Replace Cloud Services isn’t just wishful thinking—it’s grounded in breakthrough hardware innovations, software optimizations, and entirely new approaches to AI architecture that make sophisticated intelligence feasible on resource-constrained devices.
Neural Processing Units (NPUs): Modern smartphones, laptops, and tablets now include dedicated AI processors called NPUs or neural engines. These specialized chips handle AI workloads far more efficiently than traditional CPUs or GPUs, performing trillions of operations per second while consuming minimal power. Apple’s Neural Engine, Qualcomm’s Hexagon processors, and Google’s Tensor chips represent this new category of silicon explicitly designed for AI inference.
Model Compression Techniques: AI researchers have developed revolutionary methods to shrink massive models without significant performance degradation. Quantization reduces model precision from 32-bit to 8-bit or even 4-bit, cutting model size by 75-90%. Pruning removes unnecessary neural network connections, and knowledge distillation transfers capabilities from large “teacher” models to compact “student” models that run efficiently on devices.
Efficient Architectures: New AI architectures like MobileNet, EfficientNet, and transformer variants designed for edge computing deliver impressive performance with dramatically fewer parameters. These architectures achieve similar results to larger models while requiring exponentially less memory and computation—perfect for device-based deployment.
Hardware-Software Co-Design: The most effective On-Device AI solutions emerge from tight integration between hardware capabilities and software optimization. Apple’s approach with iOS and their custom silicon demonstrates how vertically integrated systems can extract maximum performance from limited resources.
Advanced Memory Management: Innovations in how AI models are loaded, cached, and executed in memory enable devices to run models that would seemingly exceed their capacity. Techniques like dynamic model loading, memory swapping, and attention mechanism optimization make the impossible routine.
1. Privacy Advantages Driving the Shift to On-Device AI
Perhaps the most compelling reason On-Device AI Will Replace Cloud Services is privacy. In an era of increasing data breaches, surveillance concerns, and regulatory scrutiny, keeping AI computation local isn’t just convenient—it’s necessary.
Zero Data Transmission: When AI processing happens entirely on your device, your personal information never travels across networks where it could be intercepted, logged, or leaked. Your photos, messages, voice commands, and documents remain under your exclusive control. This fundamental architecture shift eliminates entire categories of privacy risks.
Regulatory Compliance Simplified: GDPR in Europe, CCPA in California, and similar regulations worldwide impose strict requirements on how companies handle personal data. On-Device AI elegantly sidesteps many compliance challenges because data processing occurs locally, reducing regulatory burden and liability for companies.
No Server-Side Data Storage: Cloud AI services typically store your data for varying periods—sometimes indefinitely—to improve models, provide service history, or for other business purposes. On-Device AI Will Replace Cloud Services partly because it eliminates this storage entirely. Your data exists only on your device under your control.
Protection from Data Breaches: Major cloud services suffer data breaches regularly, exposing millions of users’ information. When AI runs on-device, there’s no central honeypot of user data for hackers to target. The attack surface shrinks from millions of users to individual devices.
Sensitive Use Cases Enabled: Medical AI applications, legal document analysis, financial planning tools, and other privacy-critical use cases become viable when users trust their data won’t leave their devices. On-Device AI unlocks entire categories of applications previously deemed too risky for cloud deployment.
Corporate and Government Adoption: Organizations handling classified information, trade secrets, or sensitive personal data increasingly require on-device AI solutions. The defense industry, healthcare systems, financial institutions, and government agencies are driving significant demand for AI that never touches external networks.
User Trust and Control: Consumers increasingly understand privacy implications and prefer services that respect their data. Companies offering On-Device AI solutions gain competitive advantage through demonstrable privacy protection that builds user trust.
2. Performance Benefits: Speed and Reliability Without the Cloud
Beyond privacy, On-Device AI Will Replace Cloud Services because local processing delivers superior user experiences in terms of speed, reliability, and consistency.
Elimination of Network Latency: Cloud AI requires data to travel to remote servers and back, introducing latency that ranges from barely noticeable to frustratingly slow depending on network conditions. On-Device AI processes requests in milliseconds, enabling real-time applications that feel instantaneous.
Consistent Performance: Your experience with cloud services varies dramatically based on internet speed, server load, and network congestion. On-Device AI delivers consistent performance regardless of external factors, providing reliable experiences users can depend on.
Offline Functionality: Perhaps the most transformative aspect of On-Device AI is its ability to work without any internet connection. On airplanes, in remote areas, during internet outages, or in countries with restricted connectivity, your AI capabilities remain fully functional.
Reduced Bandwidth Consumption: Sending data to the cloud and receiving results consumes significant bandwidth. On-Device AI Will Replace Cloud Services partly because it eliminates this data transfer, reducing costs for users with limited data plans and decreasing network congestion.
Battery Efficiency: While it seems counterintuitive, On-Device AI can be more battery-efficient than cloud solutions. Network transmission consumes substantial power, and optimized on-device inference on dedicated AI hardware often uses less energy than maintaining constant cloud connectivity.
Scalability Without Infrastructure: Cloud services require massive infrastructure investments that scale with user growth. On-Device AI leverages the processing power users already carry, distributing computational load across billions of devices rather than centralizing it in data centers.
Real-Time Processing: Applications requiring immediate responses—augmented reality, live translation, autonomous driving assistance, or real-time video enhancement—benefit enormously from On-Device AI’s instant processing without round-trip network delays.
3. Cost Implications: Economic Forces Behind the Transition
The economics of AI deployment are shifting in ways that make On-Device AI Will Replace Cloud Services not just technically feasible but financially inevitable.
Cloud Computing Costs: Running AI in the cloud is expensive. Companies pay for server compute time, data storage, bandwidth, and infrastructure maintenance. These costs scale with usage, making successful products increasingly expensive to operate. On-Device AI shifts these costs from recurring operational expenses to one-time device hardware costs.
Bandwidth Savings: Every interaction with cloud AI consumes bandwidth that companies must pay for. With millions or billions of requests, bandwidth costs become substantial. On-Device AI Will Replace Cloud Services because local processing eliminates these ongoing expenses entirely.
Reduced Infrastructure Requirements: Cloud AI requires massive data centers with cooling systems, security, redundancy, and maintenance. These capital-intensive facilities represent enormous fixed costs. On-Device AI leverages devices users already own, eliminating most infrastructure investment.
Margin Improvement for Hardware Manufacturers: Device makers can differentiate products through AI capabilities that don’t require subscriptions or ongoing service fees. This creates better unit economics and customer satisfaction compared to cloud-dependent features requiring perpetual connectivity.
Subscription Fatigue: Consumers are growing weary of subscription-based services for every feature. On-Device AI enables companies to offer premium AI features as permanent device capabilities rather than ongoing subscriptions, appealing to customers seeking ownership over rental.
Energy Costs: Data centers consume enormous amounts of electricity for computation and cooling. As energy costs rise and environmental concerns intensify, the distributed computing model of On-Device AI becomes increasingly attractive from both cost and sustainability perspectives.
Democratization of AI: When On-Device AI Will Replace Cloud Services, AI capabilities become available to users regardless of ability to pay ongoing fees. This democratization expands the potential market while reducing barriers to adoption.
4. Industries Being Transformed by On-Device AI
The shift toward On-Device AI isn’t happening uniformly—certain industries are leading the transformation due to specific requirements or opportunities.
Smartphone and Personal Computing: Mobile devices are the frontline of On-Device AI Will Replace Cloud Services. Features like computational photography, voice typing, language translation, and smart assistants increasingly run locally. Apple’s iOS, Google’s Android, and Samsung’s devices showcase progressively sophisticated on-device AI with each generation.
Healthcare and Medical Devices: Medical AI demands privacy, reliability, and offline functionality—perfect for on-device deployment. Diagnostic tools, continuous health monitoring, medical imaging analysis, and clinical decision support increasingly leverage On-Device AI to protect patient privacy while delivering critical functionality.
Automotive and Transportation: Autonomous vehicles can’t rely on cloud connectivity for real-time decisions. On-Device AI powers advanced driver assistance systems, navigation, predictive maintenance, and in-vehicle experiences. The automotive industry represents one of the largest deployments of edge AI globally.
Manufacturing and Industrial IoT: Factory floors, oil rigs, and remote industrial sites often lack reliable connectivity. On-Device AI Will Replace Cloud Services in these environments by enabling predictive maintenance, quality control, safety monitoring, and process optimization without cloud dependence.
Retail and Point-of-Sale: In-store AI for inventory management, customer behavior analysis, checkout automation, and personalized recommendations benefits from local processing that works during internet outages and protects customer privacy.
Smart Home and IoT: Security cameras, smart speakers, thermostats, and home automation increasingly process data locally. On-Device AI enables faster responses, works during internet outages, and prevents constant streaming of home data to cloud servers.
Education Technology: Educational AI tools deployed on student devices benefit from On-Device AI’s offline capabilities, privacy protection, and consistent performance regardless of varying network quality across different schools and homes.
Financial Services: Banking apps, fraud detection, personalized financial advice, and transaction analysis increasingly leverage On-Device AI to protect sensitive financial data while delivering sophisticated features.
5. Technical Challenges Still Being Solved
While On-Device AI Will Replace Cloud Services for many applications, significant technical challenges remain that researchers and engineers are actively addressing.
Model Size Limitations: Despite compression advances, the largest, most capable AI models still exceed device memory capacity. Techniques like model sharding, dynamic loading, and hybrid cloud-edge architectures bridge this gap, but truly massive models remain challenging for local deployment.
Power Consumption Management: AI inference, especially continuous processing, can drain batteries quickly. Optimizing models for power efficiency, leveraging specialized hardware, and intelligent task scheduling help, but battery life remains a constraint for the most demanding applications.
Heat Generation: Intensive AI computation generates heat that devices must dissipate. Smartphones and tablets lack active cooling, limiting sustained AI processing. Thermal management innovations and more efficient architectures gradually address this challenge.
Update and Improvement Cycles: Cloud AI models can be updated instantly, improving all users’ experiences simultaneously. On-Device AI requires software updates to improve models, creating version fragmentation and slower deployment of enhancements.
Specialized Domain Knowledge: Some AI applications require vast knowledge bases that don’t fit on devices. Hybrid approaches where general capabilities run locally while specialized queries use cloud resources represent one solution to this challenge.
Hardware Fragmentation: Unlike cloud services running on standardized infrastructure, On-Device AI Will Replace Cloud Services across billions of devices with varying capabilities. Optimizing models for diverse hardware creates development complexity.
Quality Assurance Complexity: Testing cloud AI involves validating a single deployment. Testing on-device AI requires validation across numerous device types, OS versions, and hardware configurations—exponentially increasing QA complexity.
6. The Hybrid Future: Combining On-Device and Cloud AI
Rather than complete replacement, the most likely scenario is that On-Device AI Will Replace Cloud Services for many tasks while cloud and edge work together for optimal results.
Tiered Processing Strategies: Simple, frequent, or privacy-sensitive tasks run on-device. Complex, infrequent, or data-intensive tasks leverage cloud resources. This tiered approach balances performance, privacy, and capability.
Cloud as Knowledge Repository: Devices might handle inference (applying AI models) locally while occasionally syncing with cloud services to access updated models, specialized knowledge, or collaborative learning without sharing raw user data.
Federated Learning: This technique allows devices to contribute to model improvement without uploading personal data. Devices train on local data and share only model updates, enabling collective intelligence while preserving privacy—a perfect bridge between on-device and cloud approaches.
Edge Computing Networks: Rather than distant data centers, AI computation might happen on nearby edge servers—at cell towers, local distribution points, or regional data centers. This approach reduces latency while maintaining some benefits of centralized processing.
Intelligent Task Routing: Future systems will automatically decide whether to process requests on-device, at the edge, or in the cloud based on real-time factors like battery level, network quality, privacy requirements, and task complexity.
Seamless Failover: When On-Device AI Will Replace Cloud Services for primary functionality, cloud services can serve as backup, providing redundancy when device resources are constrained or for tasks exceeding local capabilities.
Collaborative Processing: Some applications benefit from combining on-device and cloud AI, where devices handle real-time processing while cloud services provide deeper analysis, historical context, or collaborative features.
7. Privacy Regulations Accelerating the Transition
Legal and regulatory frameworks worldwide are accelerating the timeline for how On-Device AI Will Replace Cloud Services by creating compliance advantages for local processing.
GDPR and Data Minimization: European privacy regulations require companies to minimize data collection and processing. On-Device AI aligns perfectly with these principles, making compliance simpler and reducing regulatory risk.
Right to Data Portability: Regulations increasingly grant users rights to their data. When AI processes data entirely on-device, users inherently control their information, simplifying compliance with portability requirements.
Children’s Privacy Protections: Laws like COPPA in the US impose strict limitations on collecting data from children. On-Device AI enables educational and entertainment applications for children without the legal complexity of cloud data processing.
Healthcare Data Regulations: HIPAA in the US and similar healthcare privacy laws worldwide create significant liability for cloud processing of medical information. On-Device AI Will Replace Cloud Services in healthcare partly to avoid these compliance burdens.
Financial Data Protection: Banking and financial regulations require extensive security measures for cloud data processing. On-Device AI offers simpler compliance paths for financial applications by keeping sensitive data local.
Cross-Border Data Transfer Restrictions: Many countries restrict transferring citizen data across borders. On-Device AI eliminates these concerns entirely, enabling global applications without complex data localization strategies.
Upcoming AI-Specific Regulations: New regulations specifically addressing AI systems increasingly emphasize transparency, explainability, and user control—all easier to implement with On-Device AI than opaque cloud systems.
8. Major Tech Companies Leading the On-Device AI Revolution
Understanding which companies are investing heavily in On-Device AI reveals the strategic importance of this transition and where the technology is heading.
Apple’s Integrated Approach: Apple has pioneered On-Device AI through tight hardware-software integration. Their Neural Engine powers features like Face ID, photo enhancements, voice typing, and increasingly sophisticated Siri capabilities—all processed locally. Apple’s privacy-focused marketing emphasizes that On-Device AI Will Replace Cloud Services for most user interactions.
Google’s Hybrid Strategy: While historically cloud-focused, Google increasingly deploys On-Device AI in Android and Pixel devices. Features like live caption, on-device translation, and smart replies run locally. Google’s TPU (Tensor Processing Unit) technology extends from data centers to smartphone chips.
Qualcomm’s Enabling Technology: As the world’s largest mobile chip supplier, Qualcomm’s Snapdragon processors with integrated AI engines enable On-Device AI across countless Android devices. Their investments in efficient AI hardware accelerate the industry-wide transition.
Microsoft’s Edge AI Push: Microsoft is developing smaller language models optimized for local deployment and integrating AI capabilities into Windows that run on-device. Their investments in specialized AI hardware for PCs demonstrate belief that On-Device AI Will Replace Cloud Services even for productivity applications.
Samsung’s Device Intelligence: Samsung’s Exynos processors include powerful NPUs, and their Galaxy devices increasingly showcase on-device capabilities for photography, translation, and assistant features. Their commitment to local processing reflects consumer demand for privacy.
NVIDIA’s Edge AI Platforms: While known for cloud AI hardware, NVIDIA’s Jetson platform enables sophisticated On-Device AI for robotics, autonomous machines, and edge computing applications, showing how even GPU giants recognize the edge computing trend.
Amazon’s Surprising Shift: Despite AWS cloud dominance, Amazon develops on-device capabilities for Alexa and Ring devices, recognizing that On-Device AI Will Replace Cloud Services for latency-sensitive and privacy-critical applications.
9. Developer Tools and Frameworks Enabling the Transition
The ecosystem of tools making On-Device AI accessible to developers is rapidly maturing, accelerating adoption across applications.
TensorFlow Lite: Google’s framework for deploying machine learning models on mobile and embedded devices has become an industry standard. It enables developers to optimize and convert models for efficient on-device execution.
Core ML: Apple’s framework seamlessly integrates machine learning models into iOS, macOS, watchOS, and tvOS applications. Its optimization tools automatically prepare models for Apple’s Neural Engine.
PyTorch Mobile: Facebook’s (Meta’s) PyTorch framework now includes mobile deployment capabilities, allowing researchers and developers to transition models from training to on-device deployment efficiently.
ONNX Runtime: The Open Neural Network Exchange format enables model portability across frameworks and hardware platforms, simplifying the deployment of On-Device AI across diverse devices.
Edge Impulse: This platform democratizes On-Device AI development for embedded systems and IoT devices, providing tools for data collection, model training, and deployment without deep machine learning expertise.
Model Optimization Tools: Specialized tools for quantization, pruning, and compression help developers shrink models while maintaining accuracy, making On-Device AI Will Replace Cloud Services practically achievable.
Performance Profiling: New debugging and profiling tools help developers understand model performance on various devices, identifying bottlenecks and optimization opportunities specific to edge deployment.
10. What 2026 Will Actually Look Like
By 2026, On-Device AI Will Replace Cloud Services to an extent that will make today’s cloud-dependent AI seem as outdated as dial-up internet feels now.
Smartphone AI Capabilities: Your phone will run language models comparable to today’s GPT-3.5, generate images locally, edit videos with AI assistance, and provide real-time translation—all without internet connectivity. Battery life will improve as efficient NPUs handle these tasks more effectively than current cloud-dependent approaches.
Laptop and Desktop Computing: Personal computers will include powerful NPUs making them AI powerhouses. Complex tasks like video editing, 3D rendering, code generation, and content creation will leverage On-Device AI that rivals or exceeds today’s cloud services while protecting your intellectual property.
Wearable Intelligence: Smartwatches and AR glasses will include AI capabilities that currently require phone connectivity. Health monitoring, navigation, communication assistance, and contextual information will work independently, making wearables truly standalone devices.
Automotive AI Everywhere: Even basic vehicles will include sophisticated On-Device AI for safety features, navigation, entertainment, and driver assistance. The automotive AI market will represent one of the largest deployments of edge intelligence globally.
Smart Home Privacy: Home security cameras, smart speakers, and automation systems will process everything locally. Your home’s AI will understand context, learn preferences, and automate tasks without streaming your life to corporate servers.
Enterprise Adoption: Businesses will deploy On-Device AI for sensitive operations, reducing cloud costs, improving security, and ensuring business continuity regardless of internet availability. Hybrid approaches will balance on-device privacy with cloud-based collaboration.
Developing World Connectivity: On-Device AI Will Replace Cloud Services in regions with limited internet infrastructure, providing advanced capabilities to billions without reliable connectivity. This democratization will accelerate economic development and educational opportunities.
New Application Categories: Applications impossible today will emerge—highly personalized AI that knows you intimately without privacy concerns, creative tools that work anywhere, educational AI available to every student regardless of connectivity, and productivity enhancements that function reliably under all conditions.
Conclusion: Preparing for the On-Device AI Future
The transition where On-Device AI Will Replace Cloud Services isn’t a binary switch but a gradual shift already well underway. By 2026, the balance will have tipped decisively toward edge computing for most AI applications, though cloud services will remain important for specific use cases.
For consumers, this transformation means better privacy protection, improved performance, enhanced reliability, and offline capabilities that make technology more accessible and dependable. Your devices will become more capable while respecting your data ownership.
For businesses, On-Device AI Will Replace Cloud Services in ways that reduce operational costs, simplify compliance, improve customer trust, and enable new application categories. Companies investing in edge AI capabilities now position themselves advantageously for this inevitable transition.
For developers, the shift requires new skills, tools, and thinking. Optimizing for edge deployment, managing model updates, and designing hybrid architectures become essential capabilities. The demand for developers with On-Device AI expertise will dramatically increase.
The most important insight is that On-Device AI Will Replace Cloud Services not because cloud computing fails, but because local processing succeeds in delivering superior experiences for most applications. Privacy, performance, reliability, and economics all favor edge deployment when technically feasible.
The companies, developers, and users who recognize this trend and adapt accordingly will thrive in the transformed technological landscape of 2026 and beyond. Those clinging to cloud-centric architectures will find themselves at a competitive disadvantage as On-Device AI becomes the expected standard rather than an innovative feature.
Also read this:
The Rise of AI Product Reselling: Tools You Can Flip for Profit
Why ‘AI Companions’ Are Becoming the Most Downloaded Apps of 2025